简介
nmap是一个网络扫描和主机检测的工具,nmap用于扫描网上电脑开放的网络连接端。是网络安全不可或缺的网络安全扫描工具,可帮助识别开放端口并预防潜在的网络安全威胁。它具有准确、易于使用、灵活且具有许多高级功能。
功能
nmap命令很强大,可以用来扫描网络、主机、端口、操作系统、协议、防火墙等。这里通过他的帮助nmap -h功能来介绍nmap的常用功能。常用参数做了简单的介绍。
目标选择
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| nmap 192.168.1.230 # 扫描单个IP
nmap 192.168.1.0/24 # 扫描一个网段
nmap 192.168.1.2-10 # 扫描一个范围
nmap -iL ./iplist.txt # 扫描iplist.txt中的所有IP,一行一个
nmap -iR 5 # 随机选择5个ip进行扫描,完全不知道可能扫到谁。
nmap --exclude 192.168.1.3,192.168.1.4 # 排除这两个ip,和上面命令配合使用
nmap --excludefile ./iplist.txt # 排除文件里的ip,和上面命令配合使用
|
主机发现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| nmap -sL 192.168.1.10-50 # 他只是打印出要让他扫码的ip列表,其他的啥都不干,并没有真的扫码,所有他给出的host状态(0 hosts up)也是不对的,可以用--exclude 或--excludefile 排除一些ip。
nmap -sn 192.168.1.10-50 # 相当于只ping一下,而不具体扫码端口,用于发现在线主机
nmap -Pn 192.168.1.10-50 # 他会将所有的主机视作在线,然后进行端口扫描,跳过自动发现阶段,直接进行端口扫描。会很慢。
nmap -PS/PA/PU/PY[portlist]: 使用不同协议 TCP SYN/ACK, UDP or SCTP 发现指定端口
nmap -PE/PP/PM: ICMP echo, timestamp, and netmask request discovery probes
nmap -PO[protocol list]: IP Protocol Ping
nmap -n/-R: Never do DNS resolution/Always resolve [default: sometimes]
nmap --dns-servers 8.8.8.8 mmy83.online # 指定DNS服务器
nmap --system-dns 8.8.8.8 mmy83.online # 使用操作系统的DNS解析器
sudo nmap --traceroute mmy83.online # 跟踪每个主机的跃点路径
|
扫描技术
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| nmap -sS/sT/sA/sW/sM # TCP SYN/Connect()/ACK/Window/Maimon 扫描
nmap -sU: # UDP 扫描
nmap -sN/sF/sX: TCP Null, FIN, and Xmas 扫描
nmap --scanflags <flags>: Customize TCP scan flags
nmap -sI <zombie host[:probeport]>: Idle scan
nmap -sY/sZ: SCTP INIT/COOKIE-ECHO 扫描
nmap -sO: IP protocol 扫描
nmap -b <FTP relay host>: FTP bounce 扫描
|
端口规格和扫描顺序
1
2
3
4
5
6
| nmap -p <port ranges> # 仅扫描指定端口 格式如: -p22; -p1-65535; -p U:53,111,137,T:21-25,80,139,8080,S:9
nmap --exclude-ports <port ranges> # 从扫描中排除指定的端口,端口范围和上面的例子一样
nmap -F # 快速模式-扫描比默认扫描更少的端口
nmap -r # 按顺序扫描端口-不要随机化
nmap --top-ports <number> # 扫描指定数量的常见端口数,这个有意思的是这个顺序是怎么来的
nmap --port-ratio <ratio> # 扫描端口比<ratio>更常见,如:--port-ratio 1.5,这个有意思的是这个比例咋来的
|
服务/版本检测
1
2
3
4
5
| -sV # 探测开放端口以确定服务/版本信息
--version-intensity <level> # 从0(光)设置为9(尝试所有探头)
--version-light # 限制最可能的探头(强度2)
--version-all: Try every single probe (intensity 9)
--version-trace: Show detailed version scan activity (for debugging)
|
脚本扫描
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| -sC # 相当于--script=default
--script=<Lua scripts>: # <Lua scripts> 是以逗号分隔的目录、脚本文件或脚本类别列表
--script-args=<n1=v1,[n2=v2,...]> # 为脚本提供参数
--script-args-file=filename: provide NSE script args in a file
--script-trace: Show all data sent and received
--script-updatedb: Update the script database.
--script-help=<Lua scripts>: Show help about scripts.
<Lua scripts> is a comma-separated list of script-files or
script-categories.
|
操作系统检测
1
2
3
| -O # 启用操作系统检测
--osscan-limit # 将操作系统检测限制在有前景的目标上
--osscan-guess # 更积极地猜测操作系统
|
时间和性能
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| Options which take <time> are in seconds, or append 'ms' (milliseconds),
's' (seconds), 'm' (minutes), or 'h' (hours) to the value (e.g. 30m).
-T<0-5> # 设置计时模板(越高越快)
--min-hostgroup/max-hostgroup <size>: Parallel host scan group sizes
--min-parallelism/max-parallelism <numprobes>: Probe parallelization
--min-rtt-timeout/max-rtt-timeout/initial-rtt-timeout <time>: Specifies
probe round trip time.
--max-retries <tries>: Caps number of port scan probe retransmissions.
--host-timeout <time> # 这么长时间后放弃目标
--scan-delay/--max-scan-delay <time>: Adjust delay between probes
--min-rate <number>: Send packets no slower than <number> per second
--max-rate <number>: Send packets no faster than <number> per second
|
防火墙/IDS规避和欺骗
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| -f; --mtu <val>: fragment packets (optionally w/given MTU)
-D <decoy1,decoy2[,ME],...>: Cloak a scan with decoys
-S <IP_Address> # 假源地址
-e <iface>: Use specified interface
-g/--source-port <portnum>: Use given port number
--proxies <url1,[url2],...>: Relay connections through HTTP/SOCKS4 proxies
--data <hex string>: Append a custom payload to sent packets
--data-string <string>: Append a custom ASCII string to sent packets
--data-length <num>: Append random data to sent packets
--ip-options <options>: Send packets with specified ip options
--ttl <val>: Set IP time-to-live field
--spoof-mac <mac address/prefix/vendor name>: Spoof your MAC address
--badsum: Send packets with a bogus TCP/UDP/SCTP checksum
|
输出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| -oN/-oX/-oS/-oG <file>: Output scan in normal, XML, s|<rIpt kIddi3,
and Grepable format, respectively, to the given filename.
-oA <basename>: Output in the three major formats at once
-v: 增加详细程度(使用-vv或更多以获得更大效果)
-d: Increase debugging level (use -dd or more for greater effect)
--reason: Display the reason a port is in a particular state
--open: Only show open (or possibly open) ports
--packet-trace: Show all packets sent and received
--iflist: Print host interfaces and routes (for debugging)
--append-output: Append to rather than clobber specified output files
--resume <filename>: Resume an aborted scan
--noninteractive: Disable runtime interactions via keyboard
--stylesheet <path/URL>: XSL stylesheet to transform XML output to HTML
--webxml: Reference stylesheet from Nmap.Org for more portable XML
--no-stylesheet: Prevent associating of XSL stylesheet w/XML output
|
其他
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| -6 # 开启 IPv6 扫描
-A # 启用操作系统检测、版本检测、脚本扫描和跟踪路由
--datadir <dirname>: Specify custom Nmap data file location
--send-eth/--send-ip: Send using raw ethernet frames or IP packets
--privileged: Assume that the user is fully privileged
--unprivileged: Assume the user lacks raw socket privileges
-V: 打印版本
-h: 打印帮助
|
例子
1
2
3
| nmap -v -A scanme.nmap.org # 增加详细程度(使用-vv或更多以获得更大效果)并且 启用操作系统检测、版本检测、脚本扫描和跟踪路由
nmap -v -sn 192.168.0.0/16 10.0.0.0/8
nmap -v -iR 10000 -Pn -p 80
|
最后
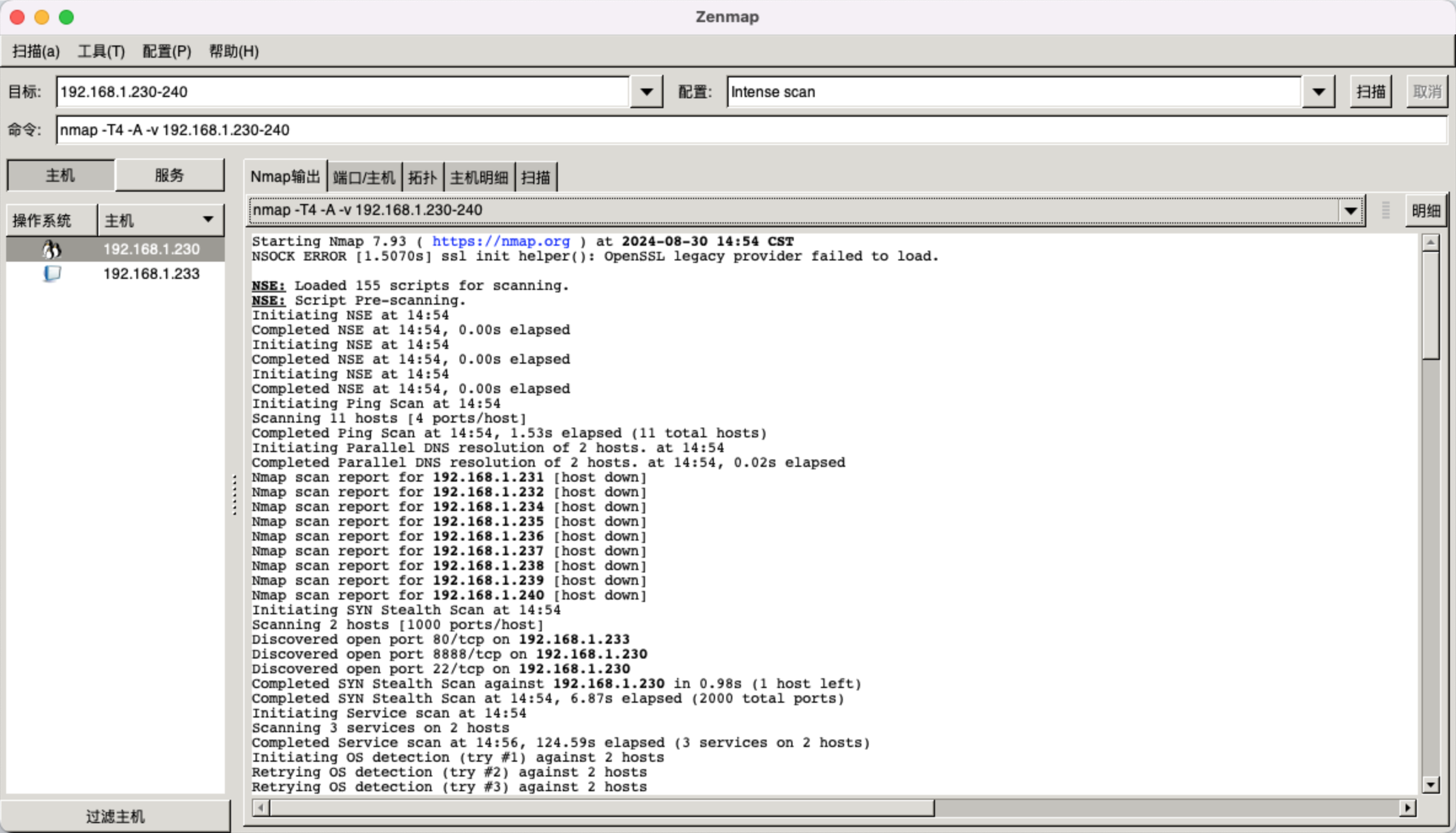
除了上面这个命令行,官网还提供一个图形界面,叫做Zenmap。使用也非常的简单,直接打开软件,然后选择扫描目标,点击开始扫描即可,更简单更直观。不知道为啥,我安装最新的版本闪退,但是旧版本可以使用。
参考