前言
我第一次接触 IPython 的时候是在《Python数据科学手册》中的第一章“IPython:超越Python”,之后就深深的喜欢上了IPython。为了感谢本书,这里推荐对数据分析感兴趣的可以看看这本书。
IPython可以直接在命令行中使用,而我更喜欢的是jupyter notebook,一个基于IPython的网页版,两者使用完全一样,因为内核就是一个东西,但是jupyter notebook是基于网页版的,这样可以不受环境限制,只要能上网就可以使用,不管是windows、linux、mac、平板、甚至手机,只要可以打开浏览器就可以使用。还有一点很重要,可以白嫖。
关于白嫖,在我知道jupyter notebook后,在自己服务器上搭建过环境,然后远程访问。但是后来发现很多的数据分析平台其实都有免费的。虽然都有限制,比如资源限制(内存、CPU);比如代码包限制,比如百度现在已经不允许用pytorch;比如运行时长限制等。毕竟商业行为,如果实在需要就只能花钱了,毕竟自己买服务器也是要花钱的,除非你花大价钱,否则还真没有免费的配置高。
推荐
上面说了白嫖,这里迫不及待的就推荐几个平台,有的可能需要科学上网。
- 百度 AI Studio:免费2核8G,更高配置需要花算力点,算力点可以买,也可以签到获得(很少就是了,但是攒一下,4核32G也可以用上俩小时)。最大的问题就是不能用除了百度自研的
飞桨之外的其他机器学习包,基础的numpy等还是有的。 - 和鲸社区:这个平台好像换了好多次名字和网址。而且也已经没有免费资源了,但是他好像有免费点数(变了好多次不知道现在还有没有),这个平台是我找到的第一个国内平台。
- Google 的 colab:这个我想大家都知道如何访问。他的代码是存放在Google云盘的。
- 玻尔®️ 科研空间站:从广告点进去的,有免费资源,就是小了点。
这些平台还提供各种学习资料及其他相关项目和数据,其实还有很多这样的平台,大部分都有免费资源或者通过签到、打卡、做任务获得免费资源。对于初学者应该很好了。如果实在需要更高资源,可能就要花钱了。
安装
上面说了,IPyhton 和 jupyter notebook其实就是一个咚咚,都是通过ipykernel这个内核实现的。一个是命令行端,一个是网页端。而且他其实就是一个pip包。
IPyhton
1
2
3
4
# 安装
pip install ipython
# 运行
ipython
jupyter notebook
1
2
3
4
5
# 安装
pip install notebook
# 启动
jupyter notebook
# 启动后,浏览器就会自动打开,如果没有打开,可以手动打开 http://127.0.0.1:8888
IPython使用技巧
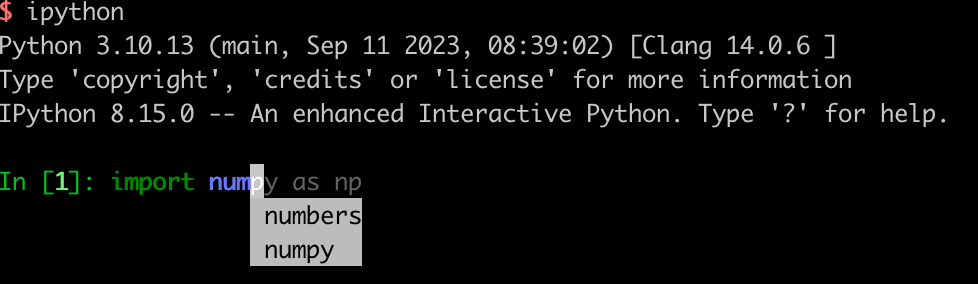
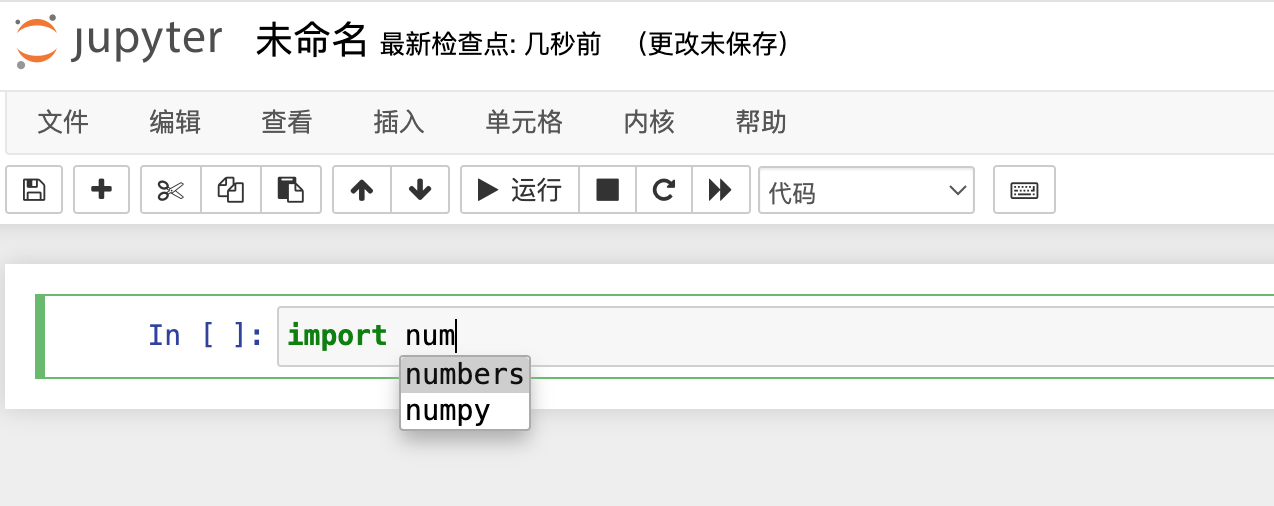
一、tab自动补齐
用惯了linux命令的这个自然不用说,应该是很习惯的,就算没用过现在的主流编辑器也都是支持自动提示的。只有写一个首字母+tab 既可以得到提醒,再也不用发愁记那些方法属性的拼写了。所有这个必须是第一个。
二、?获取文档
linux习惯了tab补齐命令,那遇到不会用的命令,咋办呢,-h、 --help、 man就应该是必不可少的。在IPython中这些都有,就是?、 ??。
- ?:前面啥也没有就直接?:打印IPython简介。按
q退出 - 对象?:内省,可以打印出该变量的详细信息。按
q退出 - 对象??:内省,打印源码,有时候也会不打印源码而是和上面一样,这是因为这个方法不是python写的。按
q退出
三、history
这个命令可以帮我们打印之前我们输入的命令。也可以用下划线方式获取历史输入和输出。
_x:x表示输出行号,所有_3就是Out[3]_:表示上一次输出__:表示倒数第二次输出_ix:x表示行号,i表示input,所有_i3,就是In [3]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
$ ipython
Python 3.10.13 (main, Sep 11 2023, 08:39:02) [Clang 14.0.6 ]
Type 'copyright', 'credits' or 'license' for more information
IPython 8.15.0 -- An enhanced Interactive Python. Type '?' for help.
In [1]: a=1+1
In [2]: a
Out[2]: 2
In [3]: b=a+1
In [4]: b
Out[4]: 3
In [5]: c=b+1
In [6]: c
Out[6]: 4
In [7]: history
a=1+1
a
b=a+1
b
c=b+1
c
history
In [8]: _
Out[8]: 4
In [9]: _6
Out[9]: 4
In [10]: _i7
Out[10]: 'history'
In [11]: __
Out[11]: 4
In [12]: exit
四、!、% 执行shell命令
在IPython中,要执行系统命令,不需要退出,只要在命令前加!,其实可以更简单,不加大部分命令也是可以执行的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
$ ipython
Python 3.10.13 (main, Sep 11 2023, 08:39:02) [Clang 14.0.6 ]
Type 'copyright', 'credits' or 'license' for more information
IPython 8.15.0 -- An enhanced Interactive Python. Type '?' for help.
In [1]: pwd
Out[1]: '/Users/mmy83'
In [2]: !pwd
/Users/mmy83
In [3]: %pwd
Out[3]: '/Users/mmy83'
In [4]:
通过上面的例子会发现,三者是不同的。直接执行命令其实是%方式执行的别名,而!执行是真的命令行执行。而且不是每一个命令都可以用这三者方式执行,比如cd,就不能用!方式执行,但是可以用%或者直接执行。因为cd或改变后续环境目录。反正我是优先直接执行,这样不行就换!方式。
%quickref 查看参考
这个命令必须要单独说一下,因为上面说的这些东西,这个命令里面都有明确说明。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
IPython -- An enhanced Interactive Python - Quick Reference Card
================================================================
obj?, obj?? : Get help, or more help for object (also works as
?obj, ??obj).
?foo.*abc* : List names in 'foo' containing 'abc' in them.
%magic : Information about IPython's 'magic' % functions.
Magic functions are prefixed by % or %%, and typically take their arguments
without parentheses, quotes or even commas for convenience. Line magics take a
single % and cell magics are prefixed with two %%.
Example magic function calls:
%alias d ls -F : 'd' is now an alias for 'ls -F'
alias d ls -F : Works if 'alias' not a python name
alist = %alias : Get list of aliases to 'alist'
cd /usr/share : Obvious. cd -<tab> to choose from visited dirs.
%cd?? : See help AND source for magic %cd
%timeit x=10 : time the 'x=10' statement with high precision.
%%timeit x=2**100
x**100 : time 'x**100' with a setup of 'x=2**100'; setup code is not
counted. This is an example of a cell magic.
System commands:
!cp a.txt b/ : System command escape, calls os.system()
cp a.txt b/ : after %rehashx, most system commands work without !
cp ${f}.txt $bar : Variable expansion in magics and system commands
files = !ls /usr : Capture system command output
files.s, files.l, files.n: "a b c", ['a','b','c'], 'a\nb\nc'
History:
_i, _ii, _iii : Previous, next previous, next next previous input
_i4, _ih[2:5] : Input history line 4, lines 2-4
exec(_i81) : Execute input history line #81 again
%rep 81 : Edit input history line #81
_, __, ___ : previous, next previous, next next previous output
_dh : Directory history
_oh : Output history
%hist : Command history of current session.
%hist -g foo : Search command history of (almost) all sessions for 'foo'.
%hist -g : Command history of (almost) all sessions.
%hist 1/2-8 : Command history containing lines 2-8 of session 1.
%hist 1/ ~2/ : Command history of session 1 and 2 sessions before current.
%hist ~8/1-~6/5 : Command history from line 1 of 8 sessions ago to
line 5 of 6 sessions ago.
%edit 0/ : Open editor to execute code with history of current session.
Autocall:
f 1,2 : f(1,2) # Off by default, enable with %autocall magic.
/f 1,2 : f(1,2) (forced autoparen)
,f 1 2 : f("1","2")
;f 1 2 : f("1 2")
Remember: TAB completion works in many contexts, not just file names
or python names.
The following magic functions are currently available:
%alias:
Define an alias for a system command.
%alias_magic:
::
%autoawait:
%autocall:
Make functions callable without having to type parentheses.
%autoindent:
Toggle autoindent on/off (deprecated)
%automagic:
Make magic functions callable without having to type the initial %.
%bookmark:
Manage IPython's bookmark system.
%cat:
Alias for `!cat`
%cd:
Change the current working directory.
%clear:
Alias for `!clear`
%code_wrap:
::
%colors:
Switch color scheme for prompts, info system and exception handlers.
%conda:
Run the conda package manager within the current kernel.
%config:
configure IPython
%cp:
Alias for `!cp`
%cpaste:
Paste & execute a pre-formatted code block from clipboard.
%debug:
::
%dhist:
Print your history of visited directories.
%dirs:
Return the current directory stack.
%doctest_mode:
Toggle doctest mode on and off.
%ed:
Alias for `%edit`.
%edit:
Bring up an editor and execute the resulting code.
%env:
Get, set, or list environment variables.
%gui:
Enable or disable IPython GUI event loop integration.
%hist:
Alias for `%history`.
%history:
::
%killbgscripts:
Kill all BG processes started by %%script and its family.
%ldir:
Alias for `!ls -F -G -l %l | grep /$`
%less:
Alias for `!less`
%lf:
Alias for `!ls -F -l -G %l | grep ^-`
%lk:
Alias for `!ls -F -l -G %l | grep ^l`
%ll:
Alias for `!ls -F -l -G`
%load:
Load code into the current frontend.
%load_ext:
Load an IPython extension by its module name.
%loadpy:
Alias of `%load`
%logoff:
Temporarily stop logging.
%logon:
Restart logging.
%logstart:
Start logging anywhere in a session.
%logstate:
Print the status of the logging system.
%logstop:
Fully stop logging and close log file.
%ls:
Alias for `!ls -F -G`
%lsmagic:
List currently available magic functions.
%lx:
Alias for `!ls -F -l -G %l | grep ^-..x`
%macro:
Define a macro for future re-execution. It accepts ranges of history,
%magic:
Print information about the magic function system.
%man:
Alias for `!man`
%matplotlib:
::
%mkdir:
Alias for `!mkdir`
%more:
Alias for `!more`
%mv:
Alias for `!mv`
%notebook:
::
%page:
Pretty print the object and display it through a pager.
%paste:
Paste & execute a pre-formatted code block from clipboard.
%pastebin:
Upload code to dpaste.com, returning the URL.
%pdb:
Control the automatic calling of the pdb interactive debugger.
%pdef:
Print the call signature for any callable object.
%pdoc:
Print the docstring for an object.
%pfile:
Print (or run through pager) the file where an object is defined.
%pinfo:
Provide detailed information about an object.
%pinfo2:
Provide extra detailed information about an object.
%pip:
Run the pip package manager within the current kernel.
%popd:
Change to directory popped off the top of the stack.
%pprint:
Toggle pretty printing on/off.
%precision:
Set floating point precision for pretty printing.
%prun:
Run a statement through the python code profiler.
%psearch:
Search for object in namespaces by wildcard.
%psource:
Print (or run through pager) the source code for an object.
%pushd:
Place the current dir on stack and change directory.
%pwd:
Return the current working directory path.
%pycat:
Show a syntax-highlighted file through a pager.
%pylab:
::
%quickref:
Show a quick reference sheet
%recall:
Repeat a command, or get command to input line for editing.
%rehashx:
Update the alias table with all executable files in $PATH.
%reload_ext:
Reload an IPython extension by its module name.
%rep:
Alias for `%recall`.
%rerun:
Re-run previous input
%reset:
Resets the namespace by removing all names defined by the user, if
%reset_selective:
Resets the namespace by removing names defined by the user.
%rm:
Alias for `!rm`
%rmdir:
Alias for `!rmdir`
%run:
Run the named file inside IPython as a program.
%save:
Save a set of lines or a macro to a given filename.
%sc:
Shell capture - run shell command and capture output (DEPRECATED use !).
%set_env:
Set environment variables. Assumptions are that either "val" is a
%store:
Lightweight persistence for python variables.
%sx:
Shell execute - run shell command and capture output (!! is short-hand).
%system:
Shell execute - run shell command and capture output (!! is short-hand).
%tb:
Print the last traceback.
%time:
Time execution of a Python statement or expression.
%timeit:
Time execution of a Python statement or expression
%unalias:
Remove an alias
%unload_ext:
Unload an IPython extension by its module name.
%who:
Print all interactive variables, with some minimal formatting.
%who_ls:
Return a sorted list of all interactive variables.
%whos:
Like %who, but gives some extra information about each variable.
%xdel:
Delete a variable, trying to clear it from anywhere that
%xmode:
Switch modes for the exception handlers.
%%!:
Shell execute - run shell command and capture output (!! is short-hand).
%%HTML:
Alias for `%%html`.
%%SVG:
Alias for `%%svg`.
%%bash:
%%bash script magic
%%capture:
::
%%code_wrap:
::
%%debug:
::
%%file:
Alias for `%%writefile`.
%%html:
::
%%javascript:
Run the cell block of Javascript code
%%js:
Run the cell block of Javascript code
%%latex:
Render the cell as a block of LaTeX
%%markdown:
Render the cell as Markdown text block
%%perl:
%%perl script magic
%%prun:
Run a statement through the python code profiler.
%%pypy:
%%pypy script magic
%%python:
%%python script magic
%%python2:
%%python2 script magic
%%python3:
%%python3 script magic
%%ruby:
%%ruby script magic
%%script:
::
%%sh:
%%sh script magic
%%svg:
Render the cell as an SVG literal
%%sx:
Shell execute - run shell command and capture output (!! is short-hand).
%%system:
Shell execute - run shell command and capture output (!! is short-hand).
%%time:
Time execution of a Python statement or expression.
%%timeit:
Time execution of a Python statement or expression
%%writefile:
::
总结
学习 Linux 的时候我就不太会记住那些命令,尤其是那些参数特别多的命令,所有经常会使用man、-h、--help、tab来查找文档和帮助拼写。IPython也是一样的,可以通过?、tab、%quickref来帮助我快速学习和完成拼写。当然,如果能全部记住就更好了。