简介
线程间通信又叫进程内通信,多个线程在访问互斥资源的时候相互之间发送信号或等待信号。
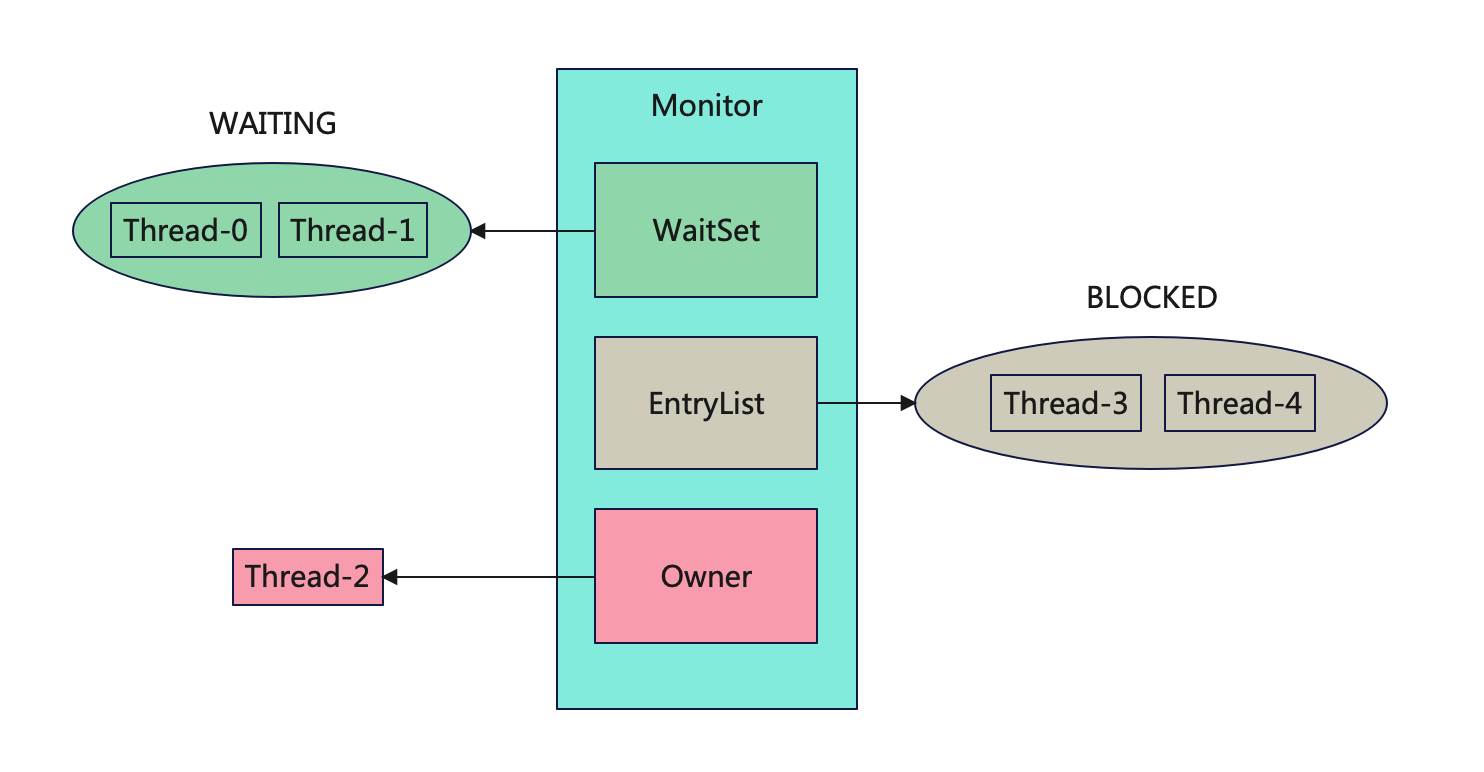
Monitor
说道线程间通信,离不开synchronized和monitor,因为他们都是在访问互斥资源的时候发生的,如果各干各的则也没必要通信了。而说道互斥资源就离不开synchronized和monitor。
synchronized实现互斥同步机制,其原理就是通过一个对象锁住代码或方法,而这个对象则关联一个Monitor。Monitor不光能锁住一段代码或一个方法,还能通过Monitor来发送信号。我们看一下Monitor的结构:
从上面的图我们可以看出Monitor结构由三部分组成:
EntryList(入口列表):当一个线程请求进入一个被锁定的对象时,它会被放置在EntryList中等待获取对象的锁。一旦对象的锁被释放,EntryList中的线程将会竞争锁的所有权。
WaitSet(等待集):WaitSet用于存放因等待某个条件而被阻塞的线程。当一个线程调用对象的wait()方法时,它会释放锁并进入等待集,直到其他线程调用notify()或notifyAll()方法来唤醒它。
Owner(所有者):Owner是当前拥有对象锁的线程。在任何时刻,只有一个线程可以成为对象锁的所有者。
synchronized就是通过Monitor的Owner和EntryList来实现线程间互斥和竞争的。而WaitSet则可以用来实现线程间通信。
wait与notify、notifyAll()
首先要说的是wait与notify不是线程的方法,而是对象的方法,每一个对象都会关联Monitor,但是并不是每一个对象都可以调用wait和notify的,只有作为synchronized锁的对象才可以,否则将抛出IllegalMonitorStateException异常。
wait:当在一个线程内调用对象的wait方法,该线程将被加入到当前对象的WaitSet集合中。当前线程放弃cpu使用权,当前对象放弃锁。也就是Owner中存的不再是当前线程,当前线程进入等待状态(WAITING或TIMED_WAITING,之所以两个是因为wait是可以有等待时间的)。
notify:当一个对象的notify被调用的时候,将会从当前对象的WaitSet集合中随机取出一个线程,注意这是随机取出的。取出的线程被放入EntryList,Owner中存的还是当前线程。
notifyAll:notifyAll与notify不同的是notifyAll会将当前对象的WaitSet集合清空,全部放入EntryList中。
示例(抄袭)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
// EventQueue.java
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class EventQueue {
private final int max;
private final static int DEFAULT_MAX_EVENT=10;
static class Event{}
private final LinkedList<Event> eventQueue = new LinkedList<>();
public EventQueue(){
this(DEFAULT_MAX_EVENT);
}
public EventQueue(int max){
this.max = max;
}
public void offer(Event event){
synchronized (eventQueue){
if (eventQueue.size()>= max){
try{
console("the queue is full");
eventQueue.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
console("the new event is submitted");
eventQueue.addLast(event);
eventQueue.notify();
}
}
public Event take(){
synchronized (eventQueue){
if(eventQueue.isEmpty()){
try{
console("the queue is empty");
eventQueue.wait();
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
Event event = eventQueue.removeFirst();
eventQueue.notify();
console("the event "+event+" is handled. ");
return event;
}
}
private void console(String s){
System.out.printf("%s:%s\n",Thread.currentThread().getName(),s);
}
}
// EventClient.java
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class EventClient {
public static void main(String[] args){
final EventQueue eventQueue = new EventQueue();
new Thread(()->{
for(;;){
eventQueue.offer(new EventQueue.Event());
}
},"Producer").start();
new Thread(()->{
for(;;){
eventQueue.take();
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(10);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"Consumer").start();
}
}
示例代码展示的是一个生产者和一个消费者进行通信,所有里面用了notify,但是如果有多个生产者和多个消费者,使用notify将不能确定唤起的是哪个线程,也就会出现问题。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
// EventQueue.java
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class EventQueue {
private final int max;
private final static int DEFAULT_MAX_EVENT=10;
static class Event{}
private final LinkedList<Event> eventQueue = new LinkedList<>();
public EventQueue(){
this(DEFAULT_MAX_EVENT);
}
public EventQueue(int max){
this.max = max;
}
public void offer(Event event){
synchronized (eventQueue){
// 将条件判断换成while
while (eventQueue.size()>= max){
try{
console("the queue is full");
eventQueue.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
console("the new event is submitted");
eventQueue.addLast(event);
eventQueue.notifyAll(); // 这里换成了notifyAll
}
}
public Event take(){
synchronized (eventQueue){
// 将条件判断换成while
while (eventQueue.isEmpty()){
try{
console("the queue is empty");
eventQueue.wait();
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
Event event = eventQueue.removeFirst();
eventQueue.notifyAll(); // 这里换成了notifyAll
console("the event "+event+" is handled. ");
return event;
}
}
private void console(String s){
System.out.printf("%s:%s\n",Thread.currentThread().getName(),s);
}
}
// EventClient.java
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class EventClient {
public static void main(String[] args){
final EventQueue eventQueue = new EventQueue();
new Thread(()->{
for(;;){
eventQueue.offer(new EventQueue.Event());
}
},"Producer1").start();
new Thread(()->{
for(;;){
eventQueue.take();
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(10);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"Consumer1").start();
// 创建多个生产者和消费者
new Thread(()->{
for(;;){
eventQueue.offer(new EventQueue.Event());
}
},"Producer2").start();
new Thread(()->{
for(;;){
eventQueue.take();
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(10);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"Consumer2").start();
}
}
注:代码来源于《java高并发编程详解》一书